Understanding Tenses in English Grammar
In English, tense is a form of a verb that indicates the time of an action or situation. For instance, tense helps us determine whether something happened in the past, is occurring now, or will happen in the future. According to the Oxford Dictionary, tense is defined as “any of the forms of a verb that show the time of the action or situation expressed by the verb.” Furthermore, tense is essential in grammar because it clarifies when events occur. By combining helping verbs like “be,” “have,” or “will” with main verbs, we can create various tenses. Therefore, using tenses correctly allows us to communicate with others more effectively and express ideas clearly.
Types of Tenses
There are three main types of tenses in English:
- Present Tense
- Past Tense
- Future Tense
Each tense has four forms:
- Simple
- Continuous
- Perfect
- Perfect Continuous
This makes a total of 12 tenses in English. Let’s explore each one and see how they work.
Explore Our Resources
📕 Download PDF eBooks Combo – इंग्लिश स्पीकिंग कोर्स की सभी पुस्तकों की eBooks का सैट
📕 Download PDF eBooks Combo (Bangla Edition)
📕 Download PDF eBooks Combo (Urdu Edition)
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- 📘 Buy Now – कम्प्लीट इंग्लिश स्पीकिंग कोर्स किट (सभी पुस्तकों का सैट + Lesson-wise वीडियो क्लासेज़ पैन्ड्राइव + नोट्स, प्रैक्टिस एवं क्विज़)
- 📚 Buy Now – इंग्लिश स्पीकिंग कोर्स की सभी पुस्तकों का सैट
- 💻 Buy Now – इंग्लिश स्पीकिंग कोर्स की Lesson-wise वीडियो क्लासेज़ पैन्ड्राइव + नोट्स, प्रैक्टिस एवं क्विज़)
- 🔴 Subscribe Now – YouTube (8M+ Subscribers)
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Present Tense
Simple Present Tense
This tense talks about actions that happen regularly or facts that are always true.
- Structure: Subject + Verb (base form/s form) + Rest of the sentence
- Example:
- She reads books every evening.
- The sun rises in the east.
Present Continuous Tense
This tense is used to describe actions happening right now.
- Structure: Subject + Helping Verb (am/is/are) + Verb + ing + Rest of the sentence
- Example:
- I am eating an apple.
- They are playing football in the park.
Present Perfect Tense
This tense shows actions that happened in the past but are still connected to the present.
- Structure: Subject + Helping Verb (have/has) + Past Participle + Rest of the sentence
- Example:
- He has finished his homework.
- We have visited that museum many times.
Present Perfect Continuous Tense
This tense talks about actions that started in the past and are still happening.
- Structure: Subject + Have/Has + Been + Verb + ing + Rest of the sentence
- Example:
- I have been studying for three hours.
- She has been learning piano since last year.
Past Tense
Simple Past Tense
This tense talks about actions that happened and were completed in the past.
- Structure: Subject + Verb (past form) + Rest of the sentence
- Example:
- He played soccer yesterday.
- They visited the zoo last weekend.
Past Continuous Tense
This tense is used for actions that were happening at a particular time in the past.
- Structure: Subject + Helping Verb (was/were) + Verb + ing + Rest of the sentence
- Example:
- She was reading a book when I arrived.
- We were cooking dinner when the power went out.
Past Perfect Tense
This tense describes an action that happened before another action in the past.
- Structure: Subject + Had + Past Participle + Rest of the sentence
- Example:
- They had already left when I reached the station.
- She had finished her exam before the bell rang.
Past Perfect Continuous Tense
This tense refers to an action that started and continued for some time before another action in the past.
- Structure: Subject + Had + Been + Verb + ing + Rest of the sentence
- Example:
- I had been waiting for an hour before the bus arrived.
- He had been practicing for weeks before the competition.
Future Tense
Simple Future Tense
This tense talks about actions that will happen in the future.
- Structure: Subject + Will/Shall + Verb (base form) + Rest of the sentence
- Example:
- We will travel to Japan next month.
- She will call you later.
Future Continuous Tense
This tense describes actions that will be happening at a particular time in the future.
- Structure: Subject + Will Be/Shall Be + Verb + ing + Rest of the sentence
- Example:
- I will be watching a movie at 8 PM.
- They will be working on the project tomorrow afternoon.
Future Perfect Tense
This tense describes actions that will be completed before a specific time in the future.
- Structure: Subject + Will Have/Shall Have + Past Participle + Rest of the sentence
- Example:
- By next year, she will have graduated from college.
- He will have finished the report by the deadline.
Future Perfect Continuous Tense
This tense talks about actions that will continue up to a certain point in the future.
- Structure: Subject + Will Have Been + Verb + ing + Rest of the sentence
- Example:
- By December, they will have been building the house for six months.
- I will have been studying for two hours by the time you arrive.
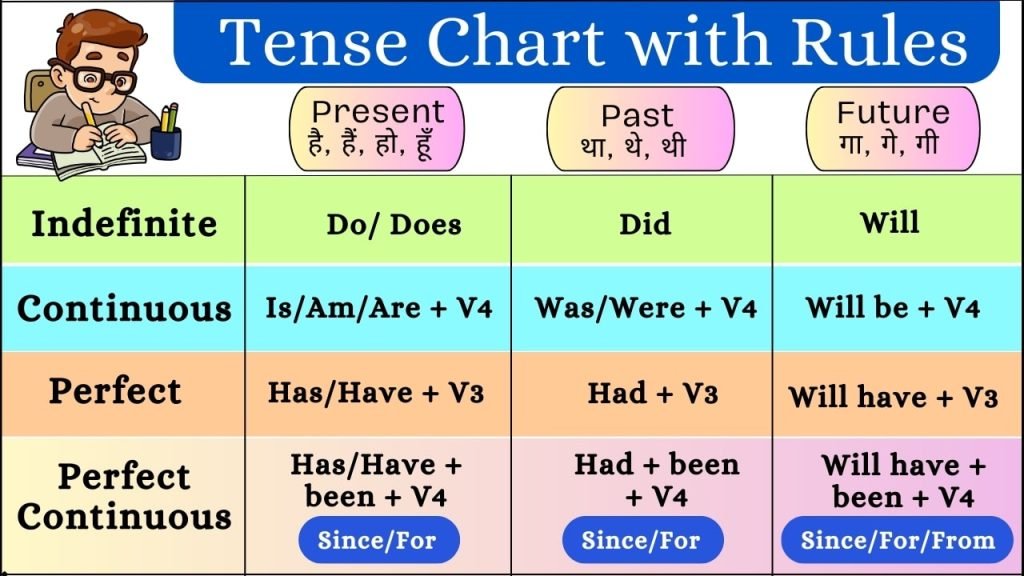
Tense Chart with Examples
Below is a summary of tenses with structures and examples:
| Tense | Structure | Example |
| Simple Present | Subject + Verb (base/s form) | He eats lunch at noon. |
| Present Continuous | Subject + am/is/are + Verb + ing | I am writing a letter. |
| Present Perfect | Subject + have/has + Past Participle | She has completed her work. |
| Present Perfect Continuous | Subject + have/has been + Verb + ing | They have been running since morning. |
| Simple Past | Subject + Verb (past form) | We played chess yesterday. |
| Past Continuous | Subject + was/were + Verb + ing | I was watching TV when she called. |
| Past Perfect | Subject + had + Past Participle | He had left before the rain started. |
| Past Perfect Continuous | Subject + had been + Verb + ing | She had been waiting for an hour. |
| Simple Future | Subject + will/shall + Verb (base) | We will visit the museum tomorrow. |
| Future Continuous | Subject + will/shall be + Verb + ing | He will be studying at this time tomorrow. |
| Future Perfect | Subject + will/shall have + Past Participle | They will have finished the work by noon. |
| Future Perfect Continuous | Subject + will/shall have been + Verb + ing | By March, she will have been teaching here for five years. |
Tips for Using Tenses Correctly
To effectively use tenses, it is important to follow a few key steps.
- First, understand the time frame by determining whether the action occurs in the past, present, or future.
- Next, choose the right tense based on the context to ensure it matches the identified time frame.
- Moreover, practicing regularly is crucial, as consistent practice helps you master the use of tenses over time.
- Lastly, pay close attention to verbs, including their forms, helping verbs, and correct usage, as they are essential for forming accurate sentences.
Conclusion
Understanding tenses is essential for clear communication in English. By using the tense chart and practicing regularly, you can improve your grammar skills and express yourself effectively in different situations. Though learning tenses may take time, the results are worth the effort. Keep practicing, and you will master them!
Common Questions About Tenses
Q1. Can tenses be mixed in a sentence?
Yes, you can mix tenses in a sentence to show a sequence of events or different time frames. For example:
- I was reading a book when he called me, and now I am finishing it.
Q2. What is the purpose of tenses in grammar?
Tenses indicate the time of an action or event and help express it clearly in speech or writing.
Q3. What are compound tenses?
Compound tenses are formed by combining auxiliary verbs like “have,” “will,” or “be” with the main verb. For example:
- She has been studying (Present Perfect Continuous).
Q4. What is the difference between future perfect and future continuous?
- Future Perfect: Shows an action that will be completed by a certain time.
- Example: She will have finished the project by 6 PM.
- Future Continuous: Describes an ongoing action in the future.
- Example: She will be working on the project at 6 PM.
Explore Our Resources
📕 Download PDF eBooks Combo – इंग्लिश स्पीकिंग कोर्स की सभी पुस्तकों की eBooks का सैट
📕 Download PDF eBooks Combo (Bangla Edition)
📕 Download PDF eBooks Combo (Urdu Edition)
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- 📘 Buy Now – कम्प्लीट इंग्लिश स्पीकिंग कोर्स किट (सभी पुस्तकों का सैट + Lesson-wise वीडियो क्लासेज़ पैन्ड्राइव + नोट्स, प्रैक्टिस एवं क्विज़)
- 📚 Buy Now – इंग्लिश स्पीकिंग कोर्स की सभी पुस्तकों का सैट
- 💻 Buy Now – इंग्लिश स्पीकिंग कोर्स की Lesson-wise वीडियो क्लासेज़ पैन्ड्राइव + नोट्स, प्रैक्टिस एवं क्विज़)
- 🔴 Subscribe Now – YouTube (8M+ Subscribers)
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
📚Trending Blogs📚
Tenses | Verbs | Prepositions | Conjunctions | Punctuation Marks | Active & Passive Voice
अगर आपको ये आर्टिकल (tenses) पसन्द आया हो, तो इसे अपने दोस्तों के साथ WhatsApp, Facebook आदि पर शेयर जरूर करिएगा। Thank you! – Aditya sir

Good article; thanks for the clarity and explanation using very simple examples.